Plug-and-Play Benchmarking of Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Large-Scale Flow Control
Abstract
FluidGym presents a standalone, fully differentiable reinforcement learning benchmark for active flow control that operates without external CFD solvers and supports standardized evaluation protocols.
Reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promising results in active flow control (AFC), yet progress in the field remains difficult to assess as existing studies rely on heterogeneous observation and actuation schemes, numerical setups, and evaluation protocols. Current AFC benchmarks attempt to address these issues but heavily rely on external computational fluid dynamics (CFD) solvers, are not fully differentiable, and provide limited 3D and multi-agent support. To overcome these limitations, we introduce FluidGym, the first standalone, fully differentiable benchmark suite for RL in AFC. Built entirely in PyTorch on top of the GPU-accelerated PICT solver, FluidGym runs in a single Python stack, requires no external CFD software, and provides standardized evaluation protocols. We present baseline results with PPO and SAC and release all environments, datasets, and trained models as public resources. FluidGym enables systematic comparison of control methods, establishes a scalable foundation for future research in learning-based flow control, and is available at https://github.com/safe-autonomous-systems/fluidgym.
Community
FluidGym: Plug-and-Play Benchmarking of Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Large-Scale Flow Control
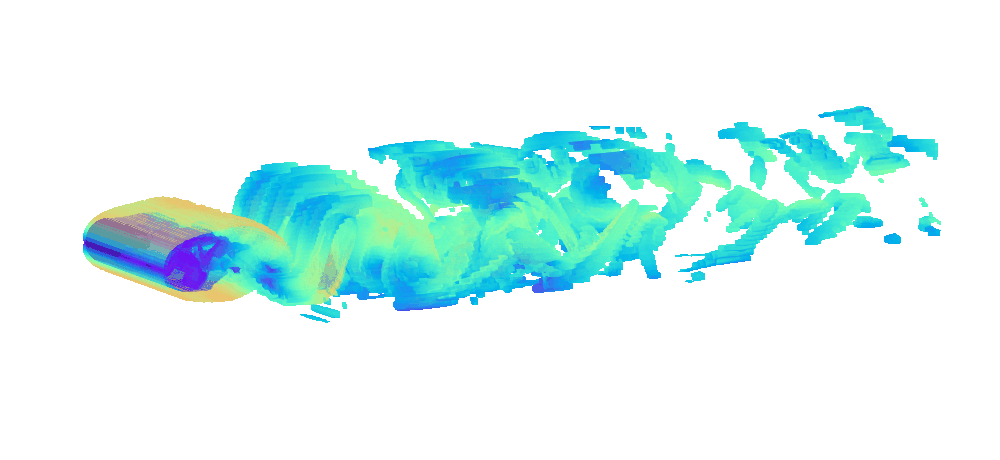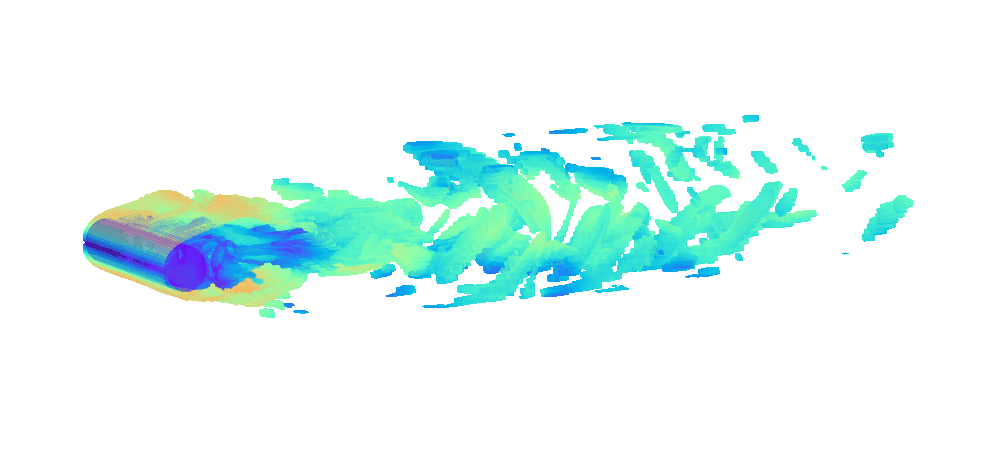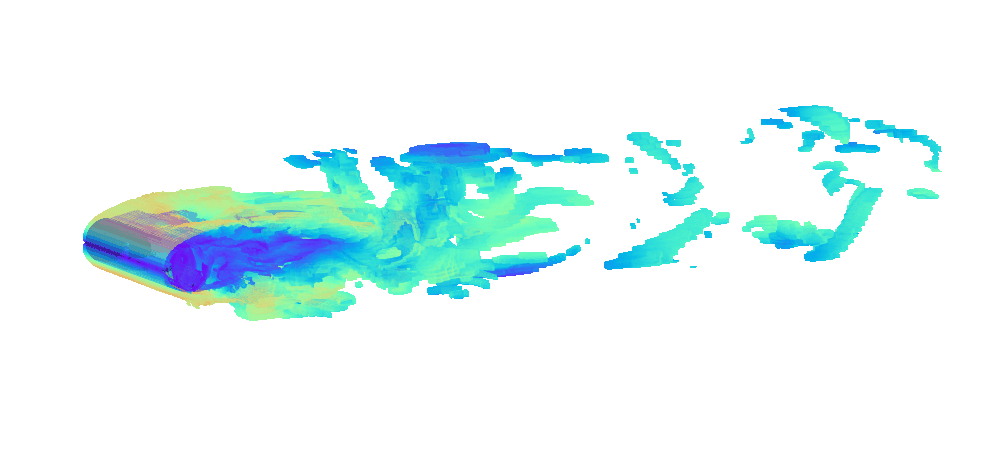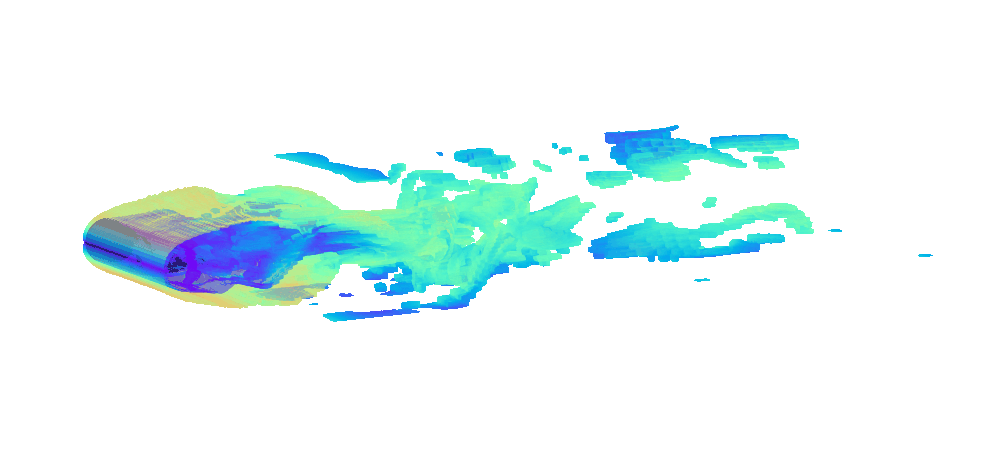
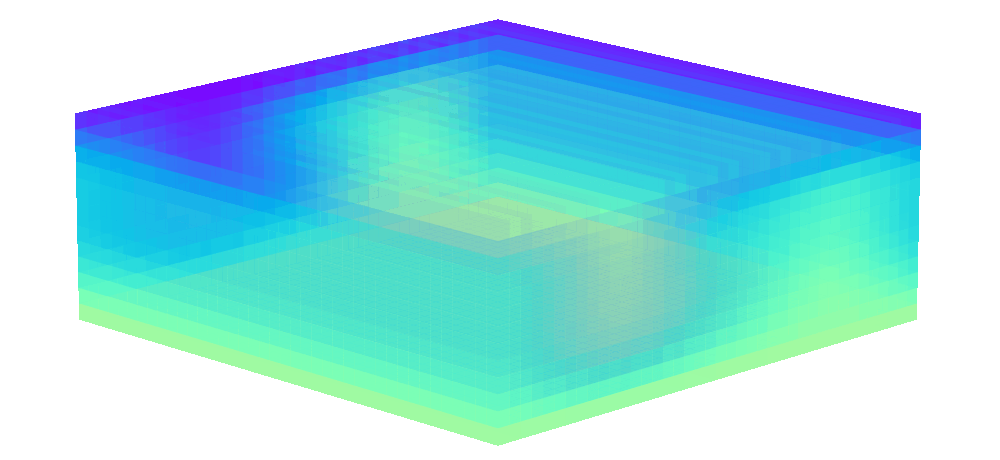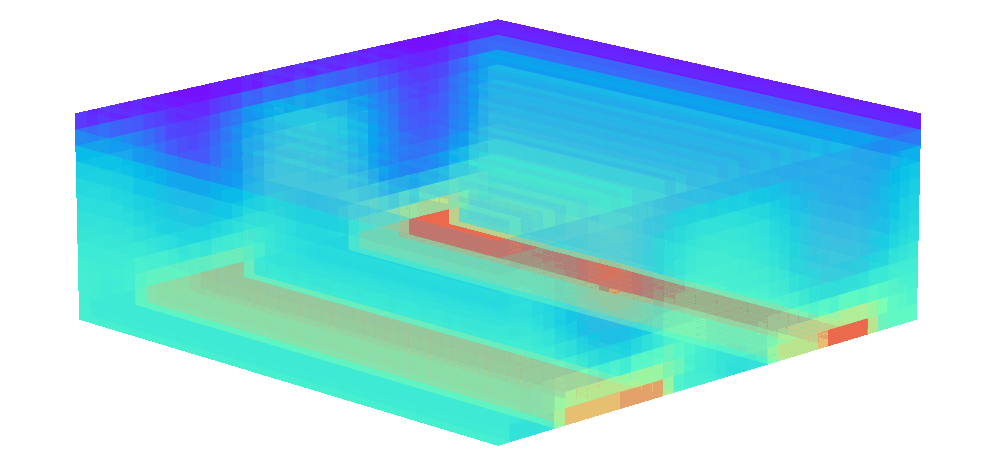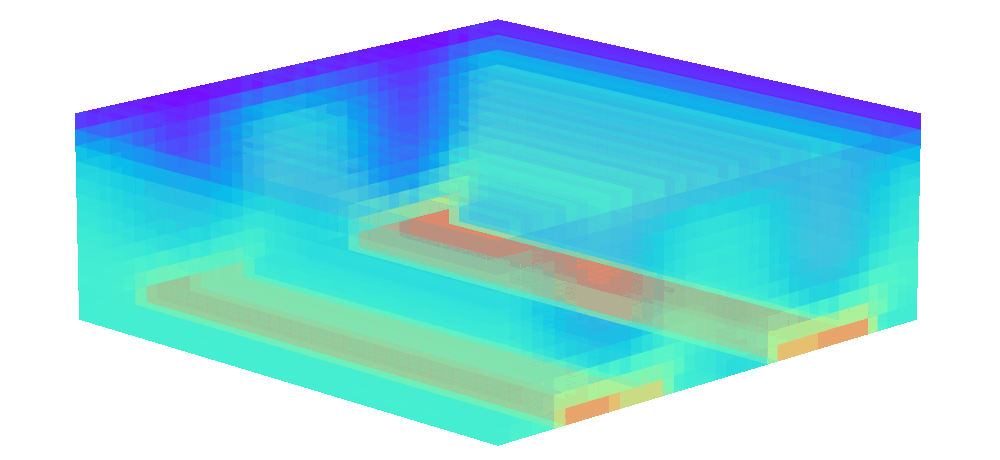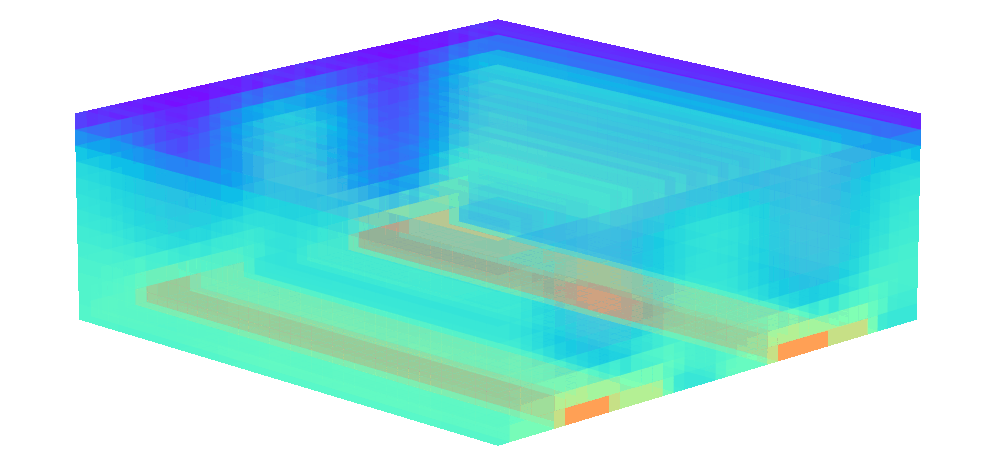
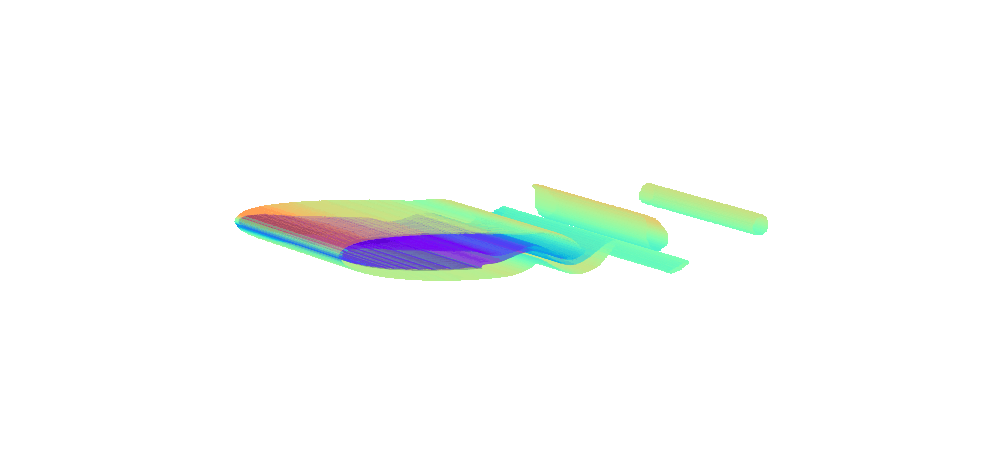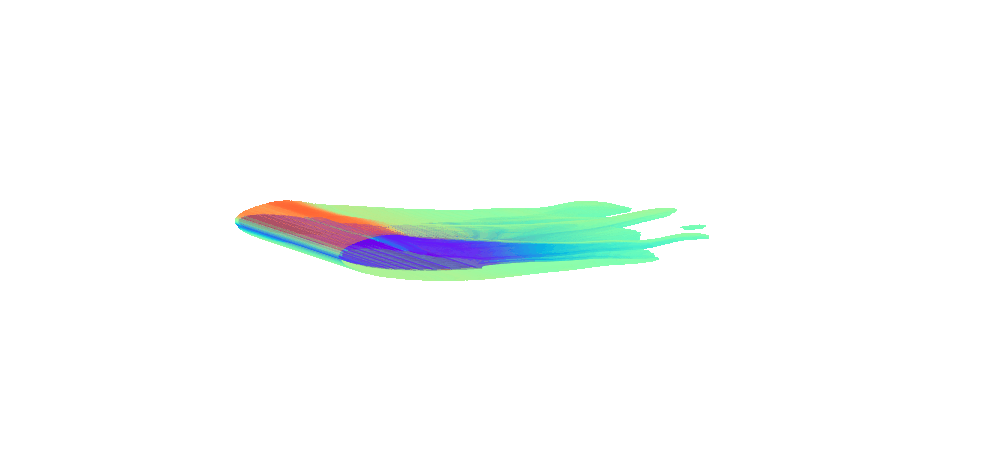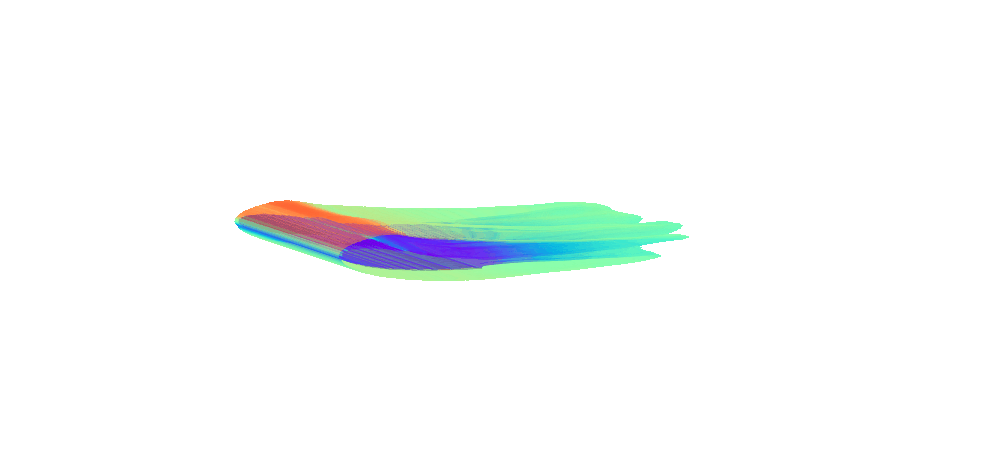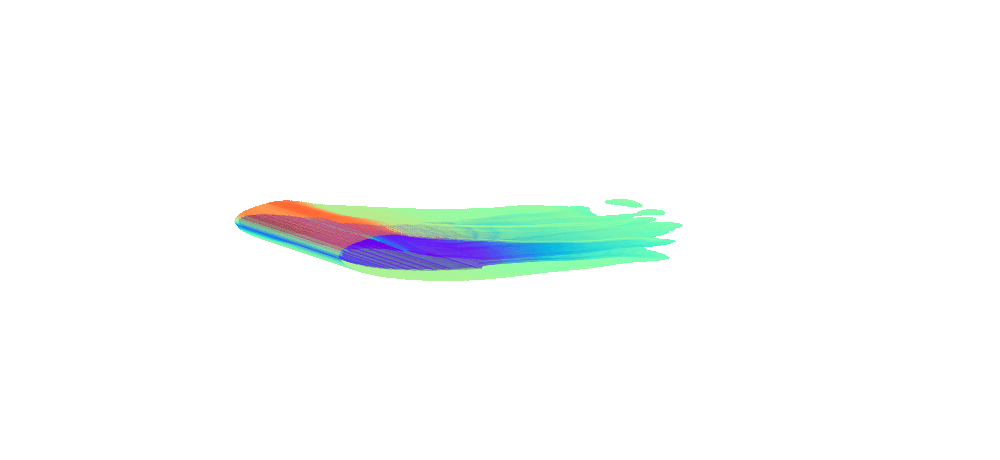
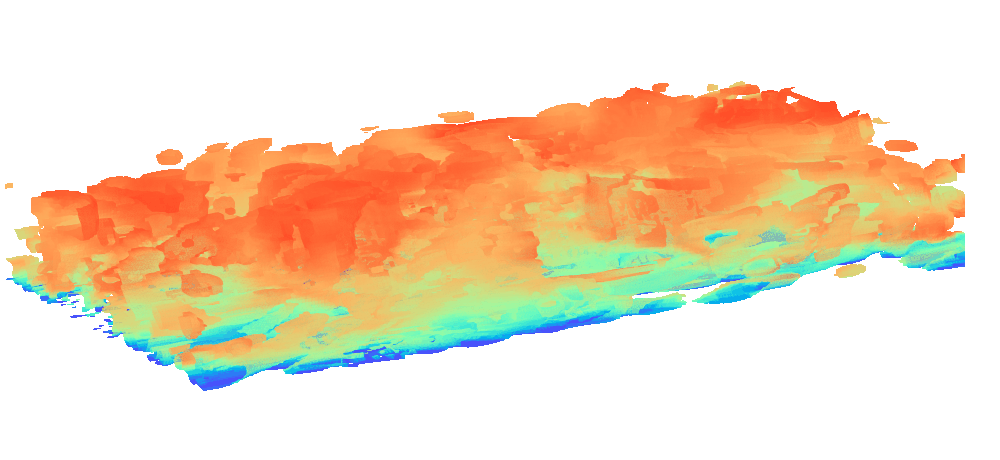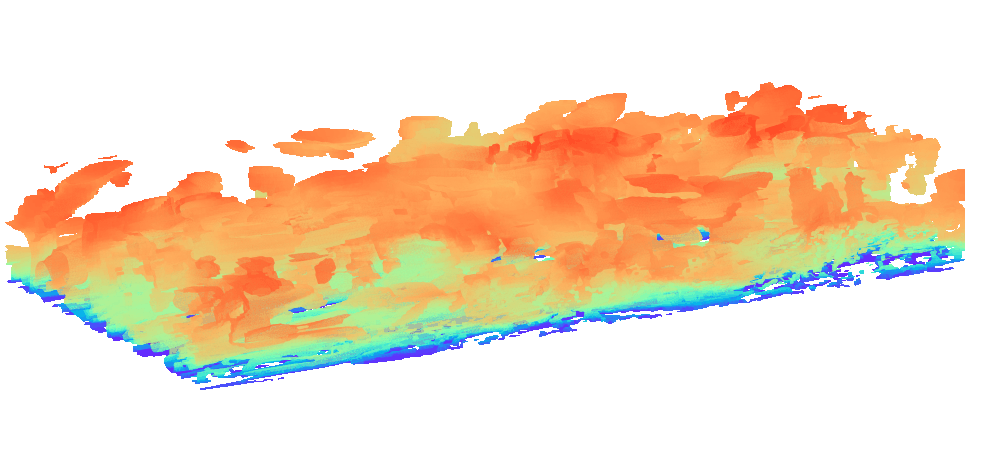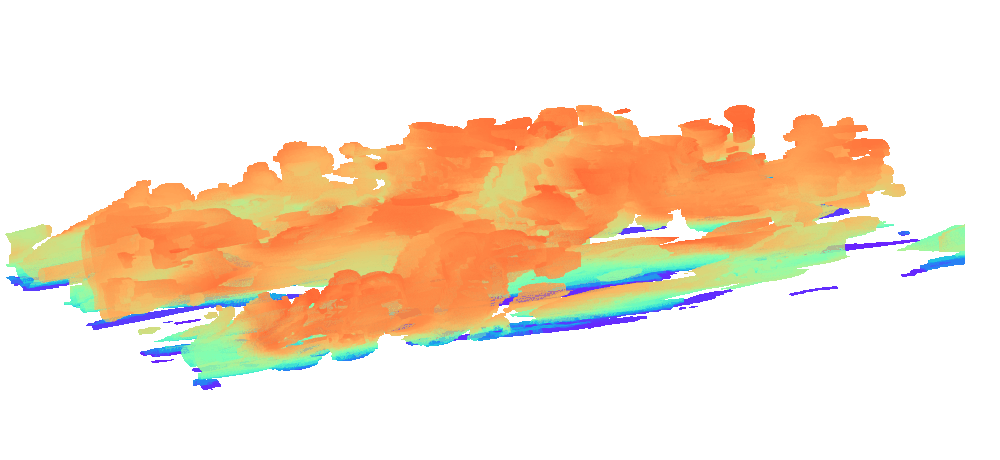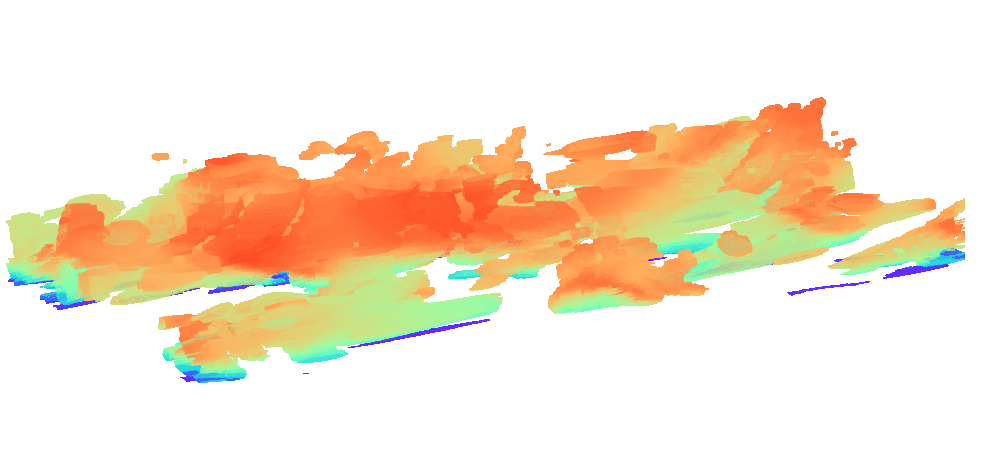
There is enormous potential for reinforcement learning and other data-driven control paradigms for controlling large-scale fluid flows. But RL research on such systems is often hindered by a complex and brittle software pipeline consisting of external solvers and multiple code bases, making this exciting field inaccessible for many RL researchers.
To tackle this challenge, we have developed a standalone, fully differentiable, plug-and-play benchmark for RL in active flow control, implemented in a single PyTorch codebase via PICT, without external solver dependencies.

We hope that this may be of interest to a large number of reinforcement learning researchers who are keen on assessing the most recent trends in basic RL research on a new set of challenging tasks, but otherwise find it difficult to enter the field of fluid mechanics
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15015v1
GitHub: https://github.com/safe-autonomous-systems/fluidgym
This is an automated message from the Librarian Bot. I found the following papers similar to this paper.
The following papers were recommended by the Semantic Scholar API
- HydroGym: A Reinforcement Learning Platform for Fluid Dynamics (2025)
- Fast Policy Learning for 6-DOF Position Control of Underwater Vehicles (2025)
- Trustworthy and Explainable Deep Reinforcement Learning for Safe and Energy-Efficient Process Control: A Use Case in Industrial Compressed Air Systems (2025)
- Coupling Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics with Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Cooperative Control of Point Absorbers (2026)
- ARISE: Adaptive Reinforcement Integrated with Swarm Exploration (2026)
- Zero-Shot MARL Benchmark in the Cyber-Physical Mobility Lab (2026)
- Guided Flow Policy: Learning from High-Value Actions in Offline Reinforcement Learning (2025)
Please give a thumbs up to this comment if you found it helpful!
If you want recommendations for any Paper on Hugging Face checkout this Space
You can directly ask Librarian Bot for paper recommendations by tagging it in a comment:
@librarian-bot
recommend
arXivlens breakdown of this paper 👉 https://arxivlens.com/PaperView/Details/plug-and-play-benchmarking-of-reinforcement-learning-algorithms-for-large-scale-flow-control-7055-f423eaec
- Executive Summary
- Detailed Breakdown
- Practical Applications
Models citing this paper 65
Browse 65 models citing this paperDatasets citing this paper 1
Spaces citing this paper 0
No Space linking this paper
